Introduction
This documentation provides a comprehensive guide of the DPF framework as well as all DPF operators available in Ansys-made DPF plugins.
The content is organized into the following sections:
- Getting started: Instructions for installing, licensing, and configuring DPF.
- User guide: Learn how to work with the server context, manage data containers and operators, explore workflow examples, and build local documentation when needed.
- Core concepts: An overview of key DPF concepts and supported data types.
- Operator specifications: Detailed reference documentation for all available operators.
Whether you are setting up DPF for the first time or looking for in-depth operator details, this guide provides the resources needed to use DPF effectively in your workflows.
Overview of DPF
The Ansys Data Processing Framework (DPF) provides numerical simulation users and engineers with a toolbox for accessing and transforming simulation data. With DPF, you can perform complex preprocessing or postprocessing of large amounts of simulation data within a simulation workflow.
DPF is an independent, physics-agnostic tool that you can plug into many apps for both data input and data output, including visualization and result plots. The following table shows an exhaustive list of solver apps supported by DPF and their related formats:
| Solver | File format | DPF version required |
|---|---|---|
| MAPDL | .rst, .mode, .rth, .rfrq, .rdsp | 1.0 (2021 R1) and later |
| MAPDL | .psd, .prs | 10.0 (2025 R2 pre0) and later |
| LS DYNA | .d3plot, .binout | 4.0 (2022 R2) and later |
| FLUENT | .cas/dat.h5, .flprj | 7.0 (2024 R1 pre0) and later |
| CFX | .res, .flprj | 7.0 (2024 R1 pre0) and later |
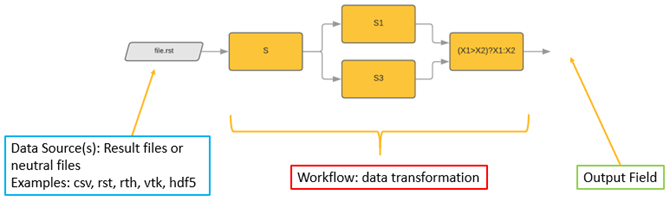
Using the many DPF operators that are available, you can manipulate and transform this data. You can also chain operators together to create simple or complex data-processing workflows that you can reuse for repeated or future evaluations.
The data in DPF is defined based on physics-agnostic mathematical quantities described in self-sufficient entities called fields. This allows DPF to be a modular and easy-to-use tool with a large range of capabilities.
Advantages
Computational efficiency
DPF is a modern framework based on new hardware architectures. Thanks to continued development, new capabilities are frequently added.
Generic interface
DPF is physics-agnostic, which means that its use is not limited to a particular field, physics solution, or file format.
Extensibility and customization
DPF is developed around two core entities:
- Data represented as a field
- An operator to act upon this data
Each DPF capability is developed through operators that allow for componentization of the framework. Because DPF is plugin-based, new features or formats can be easily added.
Install DPF
DPF is available with the Ansys installer in Ansys 2021 R1 and later, or as a pre-release DPF Server standalone package for DPF 2023 R2 and later.
-
To install DPF using the Ansys installer, download the standard Ansys installation using your preferred distribution channel, and install Ansys following the installer instructions. For information on getting a licensed copy of Ansys, visit the Ansys website.
-
The DPF Server package provides pre-releases of DPF and is independent of the Ansys installer. It is available on the DPF Pre-Release page of the Ansys Customer Portal.
See Installation in the Getting started for more information.
Operating system compatibility
DPF supports Windows 10 and Rocky Linux 8 and later. To run DPF on CentOS 7, use DPF for 2024 R2 (8.2) or later. For more information, see Ansys Platform Support.
Use DPF
You must use one of the DPF client APIs to write scripts and send commands to DPF.
DPF client APIs are currently available in three languages: C++, CPython, and IronPython (for Mechanical scripting).
The following are documentations dedicated to each:
-
HGP documentation (C++):
- DPF C++ Client library in the Developer Portal documentation for DPF.
-
PyDPF documentation (CPython):
-
Mechanical scripting (IronPython):
-
Data Processing Framework in the Scripting in Mechanical Guide.
-
Python Result in the Mechanical User's Guide.
-